
It is the repository of customer relationships, the record of financial history, the blueprint of intellectual property and the engine of future growth. The widespread migration to powerful, cloud-based SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) platforms like Zoho has been transformative, offering unprecedented levels of accessibility, collaboration and efficiency. Yet, this very convenience has given rise to a pervasive and profoundly dangerous misconception—a belief that data stored in the cloud is automatically immortal, perpetually safe and immune to loss. This is the cloud paradox: the more seamless and reliable a platform feels, the less its users tend to think about the underlying fragility of the data they entrust to it.
This illusion of automatic data safety is one of the single greatest unaddressed risks facing modern businesses. Users see that Zoho's servers are secure, that the platform is almost always available and they logically but incorrectly conclude that their data is therefore fully "backed up." They conflate platform uptime and infrastructure resilience with granular, point-in-time data recovery. They assume that because Zoho is protecting its own platform from disaster, it is also protecting their individual business from the far more common and insidious threats of human error, malicious deletion, data corruption, or catastrophic integration failures. As this comprehensive guide will demonstrate, this assumption is fundamentally flawed. Understanding the critical difference between Zoho's responsibility and your own is the first, essential step toward building a truly resilient data protection strategy that can safeguard your business's most valuable asset from permanent loss.
To truly grasp the reality of data protection in any cloud service, from Amazon Web Services to Salesforce to Zoho, one must understand the foundational concept of the Shared Responsibility Model. This principle, a cornerstone of cloud computing frequently detailed by major providers and industry analysts like Gartner, delineates the division of security and operational responsibilities between the cloud service provider (Zoho) and the customer (your business). Misunderstanding this division is the root cause of nearly every major misconception about Zoho backups.
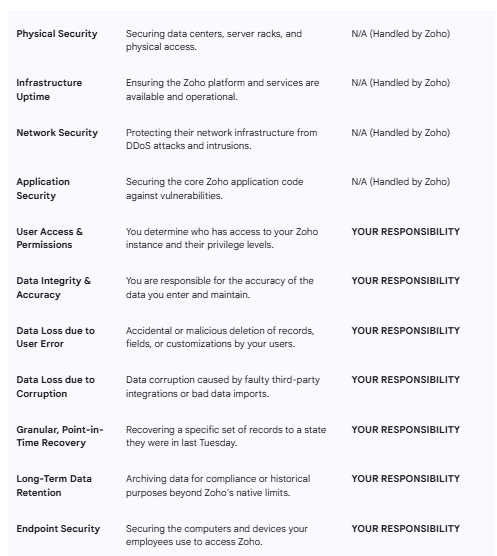
In essence, Zoho assumes responsibility for the security of the cloud. This is a massive and critical undertaking. It includes securing the physical data centers, maintaining the global network infrastructure, ensuring the core software platform is available and resilient against large-scale outages, and protecting the service from attacks targeting their infrastructure. They guarantee high uptime and have extensive disaster recovery plans for their own systems. When you use Zoho, you are benefiting from a level of infrastructure security that would be impossible for most businesses to replicate on their own.
However, the customer—your business—retains full responsibility for the security and control in the cloud. This critically includes your data. You control who has access to your Zoho instance, what permissions they have and what they do with the data inside. Consequently, Zoho is not responsible for data loss events that occur on your side of the model. These events include:
Accidental Deletion: An employee unintentionally deleting a crucial set of records, a custom module, or critical financial data.
Malicious Deletion: A disgruntled employee or a compromised user account intentionally wiping out vital information.
Data Corruption: A faulty third-party integration or a poorly executed data import that overwrites or corrupts thousands of records.
Ransomware and Malware: While Zoho's infrastructure is secure, if a user's machine is compromised and that user syncs corrupted or encrypted files, that can affect the data integrity within your Zoho instance.
Zoho's responsibility is to ensure their service is running; your responsibility is to ensure the data you put into that service is protected from loss and is recoverable to a specific point in time that meets your business needs. Their native tools, as we will explore, are designed for platform-level recovery and limited, short-term user errors—not as a comprehensive backup and disaster recovery solution for your business-critical data.

Deconstructing Zoho's Native Data Protection
To build an effective data protection strategy, it is essential to have a clear and accurate understanding of the tools Zoho itself provides. Zoho offers several native features that provide a baseline level of data protection. However, these tools are often misunderstood and are not designed to serve as a comprehensive, granular backup and recovery solution. They are primarily designed for administrative convenience, short-term error correction and Zoho's own platform-level disaster recovery. Believing these features constitute a full backup is one of the most common and dangerous mistakes a Zoho user can make.
The Recycle Bin: A Short-Term Safety Net, Not a Vault
Nearly every Zoho application, including Zoho CRM, has a Recycle Bin. When a user deletes a record, it is moved to the Recycle Bin, where it is typically stored for a limited period (e.g., 60 days) before being permanently purged.
What it is good for: The Recycle Bin is an excellent, user-friendly tool for recovering from simple, immediately-recognized accidental deletions. If an employee deletes a contact and realizes their mistake within minutes or hours, they can easily go to the Recycle Bin, find the record and restore it with a few clicks. It is a vital first line of defense against everyday human error.
What it is NOT: The Recycle Bin is fundamentally not a backup. It offers no protection against data corruption; if a record is overwritten with bad data, it is not "deleted" and therefore never enters the Recycle Bin. It offers no protection against malicious deletion by an administrator who can simply empty the Recycle Bin. Most importantly, it is temporary. Once the retention period expires, the data is gone forever, making it useless for recovering from data loss incidents that are discovered weeks or months later. It also does not protect against the deletion of customizations, such as custom fields or modules, which can be catastrophic.
Data Export: A Manual Snapshot, Not an Automated Backup
Zoho provides the ability for administrators to manually export their data from various applications, typically into CSV files. In Zoho CRM, for example, you can perform a full data export, which includes all your records from all modules.
What it is good for: Manual data exports are crucial for data portability, for creating offline copies for archival purposes, or for migrating data to another system. It provides a way to get a complete snapshot of your data at a specific moment in time, which can be useful for compliance or major data analysis projects. It is a critical feature that gives you ownership over your data.
What it is NOT: A manual export is not an automated backup strategy. It is a cumbersome, time-consuming process that relies on a human administrator remembering to perform it regularly. Because it is manual, it is prone to being forgotten, leading to large gaps between snapshots. More critically, restoring from a set of CSV files is an incredibly complex, painful and error-prone process. You would need to carefully re-import the data in the correct order to maintain relationships between records (e.g., contacts must be imported before their associated deals) and you would lose metadata, attachments and specific configurations. A CSV export is a raw data dump; it is not a restorable, point-in-time image of your Zoho environment.
A Record of Change, Not a Method of Reversal
Zoho applications maintain detailed Audit Logs that track changes made to records, showing who made a change, what they changed and when they changed it.
What it is good for: Audit Logs are an essential tool for security and accountability. They are invaluable for investigating unauthorized changes, understanding how a data corruption incident occurred or for meeting compliance requirements that mandate a detailed record of data handling.
What it is NOT: An Audit Log is not a backup or a recovery tool. It tells you that a hundred of your most valuable client records were incorrectly updated by a faulty integration last Tuesday, but it provides no mechanism to automatically revert those hundred records back to their previous state. You can see the damage, but you cannot undo it with a click of a button. The log provides the "what," but a true backup provides the "how to fix it".
Therefore, Zoho's native tools are valuable and necessary administrative features, but they do not constitute a backup strategy that can protect a business from the most common forms of data loss. They lack automation, granular point-in-time recovery and protection against corruption and malicious intent. Recognizing this distinction is the pivotal moment when a business owner realizes the need for a dedicated, third-party backup and recovery solution to truly secure their data asset. Relying solely on Zoho's native data protection features exposes a business to a range of severe and often irreversible data loss scenarios. Understanding these tangible risks is crucial for appreciating the need for a comprehensive backup strategy.
Scenario 1: The Accidental Mass Deletion or Update. An employee with broad permissions mistakenly deletes a critical custom view, or worse, uses a mass update function with the wrong criteria, incorrectly modifying thousands of contact records. The Recycle Bin won't help with the mass update and restoring thousands of individual records from the bin (if deleted) is a nightmare that loses relational data. A true backup solution could restore the affected records to their state just minutes before the error occurred.
Scenario 2: The Malicious Insider Threat. A disgruntled employee, before leaving the company, intentionally deletes critical sales pipelines, customer lists and financial records, and then empties the Recycle Bin. Without an independent, third-party backup stored outside of Zoho's control, this data is permanently and maliciously destroyed.
Scenario 3: The Faulty Third-Party Integration. A new marketing automation tool is connected to Zoho CRM. Due to a bug or misconfiguration in the integration, it systematically overwrites the "Phone Number" field for thousands of leads with incorrect data. This is data corruption, not deletion. The Recycle Bin is useless and the Audit Log only shows the damage after the fact. The only way to recover is to restore the affected records from a point-in-time backup taken before the integration was activated.
Scenario 4: The Compliance and Legal Hold Failure. A business is faced with litigation and is legally required to produce all data related to a specific client from 18 months ago. An employee involved in the case has since left and their records may have been deleted and long since purged from the Recycle Bin. Without a long-term, searchable archive provided by a third-party backup solution, the business could face severe legal penalties for failing to meet its data preservation obligations.
Scenario 5: The Catastrophic Customization Loss. An administrator accidentally deletes a complex custom module or a set of critical workflow rules that the business has spent months developing. These customizations are not 'records' and are often not recoverable through the Recycle Bin. A comprehensive backup solution that also backs up metadata and configuration settings is the only way to restore this critical operational logic.
Once a business owner accepts the critical need for a dedicated backup solution to augment Zoho's native features, the next logical step is navigating the marketplace to select the right tool. The market for SaaS backup solutions is growing and not all products are created equal. Making an informed decision requires a systematic evaluation of potential providers against a clear set of technical and operational criteria. Choosing a solution is not merely a technical purchase; it is a long-term investment in your company's resilience and data integrity. A hasty decision based solely on price can lead to a false sense of security, while a well-considered choice provides a robust safety net for your most critical asset. This buyer's guide provides a framework for US business owners to assess third-party Zoho backup solutions, ensuring the selected tool aligns with their specific recovery needs, security requirements and business continuity objectives. A truly resilient data protection strategy is a multi-layered approach that uses Zoho's native tools for what they are good at while augmenting them with a dedicated, third-party backup and recovery solution.
Layer 1: Utilize Zoho's Native Features (First Line of Defense): Continue to use the Recycle Bin for immediate, simple restores. Use Audit Logs for investigation. Perform periodic manual exports for archival purposes. This is good data hygiene.
Layer 2: Implement Automated, Third-Party Backups (The Core of the Strategy): This is the non-negotiable layer. A third-party solution should provide:
Automated, Daily Backups: Backups should run automatically every day without any human intervention.
Point-in-Time Recovery: The ability to look at snapshots of your data from any day and restore individual records, a subset of records, or your entire database to its state at that time.
Granular Restore Capabilities: The ability to restore a single record, a field within a record, or an entire module without having to perform a full system restore.
Metadata and Attachment Backup: The solution must back up not just the data in fields, but also notes, attachments and critical configuration metadata.
Independent Storage: Backups must be stored securely outside of Zoho's infrastructure, providing an air-gapped copy that is immune to issues within your Zoho instance.
Layer 3: Develop a Formal Recovery Plan: Having a backup is only half the battle. You need a documented plan that outlines:
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO): How quickly do you need to be able to restore data after a loss event?
Recovery Point Objectives (RPO): How much data are you willing to lose? (e.g., 24 hours for a daily backup).
Roles and Responsibilities: Who is authorized to initiate a restore? Who validates the data post-recovery?
Layer 4: Regular Testing and Validation: A backup strategy is not complete until it has been tested. You must regularly perform test restores to a sandbox environment to ensure that your backups are viable and that your recovery plan works as expected.
Building this multi-layered strategy is where a Zoho consulting partner like Erphub provides immense value. We can help you assess your RTO/RPO needs, select and implement the right third-party backup solution and develop and test a robust disaster recovery plan. At a minimum, any solution under consideration must deliver on a core set of features that address the fundamental gaps left by Zoho's native tools. These are the table stakes for any serious contender.
Automated, Daily Backups: The solution must perform backups automatically, at least once every 24 hours, without requiring any manual intervention from an administrator. The ability to schedule backups at a specific time (e.g., during off-peak hours) is also a valuable feature. This eliminates the risk of human error and ensures that you always have a recent recovery point.
Comprehensive Data and Metadata Coverage: A backup is only as good as what it contains. The solution must be capable of backing up not just the data within the fields of your records but also the critical context that surrounds it. This includes attachments, notes, tasks and critically, the metadata that defines your Zoho environment, such as custom fields, module layouts and workflow configurations. Losing this metadata can be just as crippling as losing the data itself, as it represents countless hours of system customization.
Granular, Point-in-Time Restore Capabilities: This is arguably the most critical feature. The provider must offer a user-friendly interface that allows you to browse your backups from any specific date. From there, you must have the ability to perform highly granular restores. This means having the options to restore a single lost record, a specific field that was overwritten across thousands of records, or an entire module, all without needing to perform a full, disruptive system-wide rollback. This surgical precision is essential for minimizing business interruption during a recovery event.
Independent, Secure Cloud Storage: The backup data must be stored in a secure cloud environment that is completely independent of Zoho's primary infrastructure. This creates an "air-gapped" copy of your data, ensuring that an issue affecting the Zoho platform (or your specific instance) will not also affect your backups. The provider should be transparent about their storage infrastructure (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) and the security measures they employ.
Security, Compliance, and Trust
You are entrusting a third party with a complete copy of your most sensitive business data. Their security and compliance posture is therefore of paramount importance.
Data Encryption (In Transit and At Rest): All backup data must be encrypted using strong, industry-standard algorithms (like AES-256) both while it is being transferred from Zoho to the backup provider's servers and while it is being stored. This is a non-negotiable security requirement.
Certifications and Compliance Adherence: The provider themselves should adhere to leading international security and privacy standards. Look for evidence of certifications like SOC 2 Type II, which audits their operational controls and security practices over time, and ISO 27001. If you operate in Europe or handle data of EU citizens, the provider must be GDPR compliant. For US healthcare organizations, their ability to sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) for HIPAA compliance is essential.
Robust Access Controls: The backup solution should have its own set of role-based access controls, allowing you to define precisely who within your organization has the authority to view backups, initiate restores, or change configuration settings.
Usability and Operational Considerations
A powerful tool that is difficult to use is a tool that will not be used effectively in a crisis.
Intuitive User Interface: The process of Browse backups, searching for specific data and initiating a restore should be simple, intuitive and fast. In the stressful moments of a data loss event, you do not want to be struggling with a complex or confusing interface.
Non-Destructive Restores: A critical feature is the ability to perform a non-destructive restore. This means the tool can restore data without overwriting any changes that have been made since the backup was taken, allowing you to merge the recovered data back into your live environment seamlessly.
Sandbox Seeding and Testing: The ability to easily restore backup data into a Zoho sandbox environment is invaluable. It allows you to test your recovery plan, validate the integrity of your backups and troubleshoot issues without any risk to your live production data.
Proactive Monitoring and Alerting: The solution should provide proactive alerts for any issues with the backup process (e.g., a failed backup job) and provide clear, comprehensive reporting on the status and health of your data protection activities.
Understanding the critical need for a robust Zoho backup strategy is the essential first step. The second and equally important, step is translating that understanding into a concrete, effective and well-managed technical solution. The journey from recognizing the risk to implementing a resilient recovery plan is fraught with technical complexities, strategic decisions and potential missteps. Navigating this journey alone can be a daunting prospect for even the most tech-savvy business owner. This is where partnering with a specialized Zoho consulting firm like Erphub becomes a strategic force multiplier, transforming a complex IT project into a seamless and successful business initiative. Our role at Erphub extends far beyond simply recommending or installing a piece of software. We act as your strategic architects for data resilience, providing end-to-end guidance and hands-on expertise to ensure your most critical asset is protected comprehensively. The Erphub advantage is built on a deep, multi-layered value proposition designed to deliver not just a solution, but confidence and peace of mind.

