
Common Manual Processes in Supply Chain Operations
The intricacies of supply chain management often involve numerous interconnected processes, many of which are still executed manually. These manual operations can create significant bottlenecks, hindering efficiency and slowing down the overall flow of goods and information.
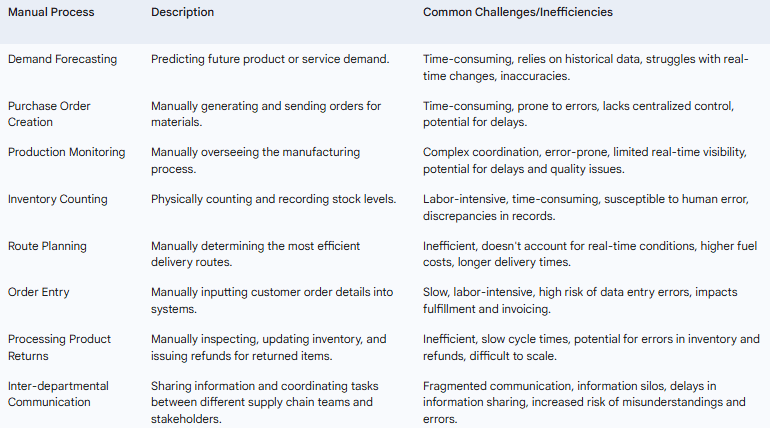
Planning and Forecasting: The initial stage of any supply chain involves meticulous planning and accurate demand forecasting. However, when these critical activities are performed manually, they often fall short of the required precision. Manual demand planning typically involves time-intensive data collection and analysis, frequently relying on historical sales figures or even subjective estimations. This approach struggles to incorporate real-time market changes, seasonal fluctuations, or emerging trends, leading to inaccuracies in predicting future demand. Consequently, businesses may face challenges in optimizing inventory levels, potentially resulting in either stockouts and lost sales or costly overstocking and increased holding expenses.
Sourcing and Procurement: Securing the necessary raw materials and components involves a complex web of interactions with vendors and suppliers. In many organizations, these crucial sourcing and procurement processes still heavily depend on manual methods. Essential tasks such as vendor proposal evaluation, contract management, and the generation of purchase orders are often handled through the exchange of spreadsheets, PDFs, and emails. This decentralized approach lacks a centralized repository for information, making it difficult to collate and compare vendor proposals efficiently. Furthermore, manual purchase order creation and approval processes can be time-consuming and prone to errors, potentially leading to delays in material acquisition and disrupting the production schedule. The absence of automated invoice matching can also result in payment discrepancies and strained vendor relationships.
Manufacturing and Production: The transformation of raw materials into finished goods is the core of the supply chain for many businesses. However, manual involvement in monitoring and coordinating production processes can introduce significant challenges. Ensuring a smooth flow of materials, managing production schedules across multiple suppliers, and coordinating timely deliveries are complex tasks that become increasingly difficult to manage without automation. Manual monitoring of production lines may not provide real-time visibility into potential bottlenecks or quality issues, leading to delays in identifying and rectifying problems. Coordinating production and delivery schedules with numerous suppliers through manual communication methods can also be cumbersome and error-prone, potentially resulting in production delays or incurring extra storage costs due to misaligned deliveries.
Inventory Management and Warehousing: Maintaining optimal inventory levels and efficiently managing warehouse operations are critical for meeting customer demand without incurring excessive costs. Manual inventory management practices often involve employees physically counting stock and recording information on paper or in spreadsheets. This approach is not only labor-intensive and time-consuming but also highly susceptible to human error, leading to inaccuracies in inventory records. Discrepancies between recorded and actual stock levels can result in stockouts, causing lost sales and customer dissatisfaction, or overstocking, tying up valuable capital and increasing warehousing costs. Furthermore, manual processes in warehouse operations, such as locating items for order picking and managing storage space, can be inefficient and contribute to longer fulfillment times.
Logistics and Transportation: The movement of goods from manufacturing facilities to distribution centers and ultimately to customers is a critical link in the supply chain. However, relying on manual processes for dispatching, route planning, and shipment tracking can lead to significant inefficiencies. Manually planning transportation routes without considering real-time traffic conditions or optimizing for fuel efficiency can result in increased delivery times and higher transportation costs. Similarly, manually contacting and coordinating with carriers to arrange shipments is a time-consuming process, especially for businesses with a high volume of deliveries. The lack of automated shipment tracking can also lead to a reactive approach to managing potential delays, impacting customer service and overall supply chain reliability.
Order Processing and Fulfillment: Efficiently processing customer orders and ensuring timely fulfillment are essential for maintaining customer satisfaction. However, manual order entry, often involving customer service representatives typing in purchase orders by hand, is a slow and labor-intensive process. This manual approach increases the risk of data entry errors, such as incorrect quantities or shipping addresses, which can lead to costly rework and customer dissatisfaction. Delays in order management due to manual processing can also push back fulfillment timelines, impacting invoicing and ultimately delaying revenue recognition. Furthermore, manually coordinating order picking, packing, and shipping processes across different departments can be inefficient and prone to communication breakdowns.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics): Handling product returns, also known as reverse logistics, is an increasingly important aspect of supply chain management, particularly with the growth of e-commerce. However, many businesses still rely on manual processes for managing returns, which can lead to inefficiencies and errors. Manual inspection of returned items, updating inventory records, and processing refunds are time-consuming tasks that are susceptible to human error. Slow cycle times in returns processing can negatively impact customer satisfaction, while inaccuracies in inventory adjustments can lead to further discrepancies in stock levels. Additionally, the lack of automated workflows for managing the reverse logistics process can make training new employees more difficult.
Communication and Collaboration: Effective supply chain management necessitates seamless communication and collaboration among various stakeholders, including internal teams, suppliers, and customers. However, reliance on manual methods often results in fragmented communication and information silos. Important information regarding production schedules, shipment statuses, or potential delays may not be readily accessible to all relevant parties, leading to misunderstandings, confusion, and ultimately, mistakes. The lack of a centralized platform for communication and collaboration can also hinder the ability to make informed decisions quickly and respond effectively to changes in the supply chain.
Automation for Processes in Supply Chain Operations
The integration of automation technologies into supply chain operations offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly accelerate a business's performance and provide a distinct competitive advantage. By replacing manual, repetitive tasks with automated systems, companies can unlock new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: One of the most immediate impacts of supply chain automation is a substantial increase in operational efficiency and overall productivity. Automation streamlines critical processes such as inventory management, order processing, and transportation logistics, allowing businesses to accelerate their workflows and improve their responsiveness to market demands. By reducing reliance on manual tasks, employees can be redirected towards more strategic and value-added activities, leading to a more agile and streamlined supply chain. This increased efficiency manifests in various ways, including higher fill rates, decreased cycle times, and increased warehouse throughput.
Reduced Errors and Improved Accuracy: Human error is an inherent limitation of manual processes, often leading to costly mistakes and inefficiencies. Automating these tasks significantly minimizes the risk of such errors, resulting in improved accuracy and consistency across various supply chain operations. From data entry and order fulfillment to inventory management and shipping, automation ensures that tasks are executed with precision, reducing discrepancies, rework, and ultimately enhancing the reliability of the entire supply chain.
Cost Reduction: The implementation of supply chain automation can lead to significant cost savings in numerous areas. By automating repetitive tasks, businesses can reduce their reliance on manual labor, leading to lower labor costs. Furthermore, the increased accuracy and efficiency resulting from automation help to minimize errors, reduce material waste, and optimize resource allocation, contributing to a more cost-effective overall supply chain operation. The ability to manage inventory levels more effectively through automation also prevents overstocking or stockouts, further contributing to cost reduction.
Enhanced Visibility and Transparency: A lack of visibility into the complexities of the supply chain is a common challenge for businesses relying on manual processes. Automation technologies provide real-time insights into all aspects of the supply chain, enhancing transparency and enabling better monitoring and decision-making. Automated systems can track inventory levels, order statuses, and shipment locations in real-time, providing a comprehensive view of the entire supply chain. This enhanced visibility allows businesses to identify potential bottlenecks or disruptions proactively, enabling timely interventions and more informed strategic decisions.
Improved Agility and Responsiveness: In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, the ability to adapt quickly to changes in demand, market conditions, and unexpected disruptions is crucial. Supply chain automation empowers businesses with greater agility and responsiveness. By automating key processes and providing real-time data, companies can react more swiftly to fluctuations in customer demand, adjust production schedules dynamically, and reroute shipments efficiently in response to unforeseen events. This enhanced agility allows businesses to maintain operational continuity and minimize the impact of disruptions on their supply chain.
Better Customer Satisfaction: Ultimately, the success of any supply chain is measured by its ability to meet customer needs effectively. Automation plays a vital role in improving customer satisfaction by ensuring faster order processing, more reliable delivery times, and enhanced communication. Automated systems can provide customers with real-time updates on their order status and estimated delivery times, increasing transparency and building trust. Furthermore, the reduced errors and improved efficiency resulting from automation contribute to more accurate order fulfillment and fewer delays, leading to a more positive overall customer experience.
Scalability and Growth: Businesses aiming for growth and expansion often find that manual processes become significant limitations. Automation provides the necessary infrastructure to scale operations efficiently without being constrained by the capacity of manual workflows. Automated systems can handle increased volumes of transactions, manage larger inventories, and process more orders without requiring a proportional increase in labor or operational costs. This scalability allows businesses to accommodate growth and adapt to changing market demands more effectively, ensuring that their supply chain can support their expansion plans.
Enhanced Employee Satisfaction: Beyond the direct operational benefits, supply chain automation can also have a positive impact on employee morale and job satisfaction. By automating repetitive and mundane tasks, automation frees up employees from tedious work, allowing them to focus on more engaging and strategic responsibilities that require their unique skills and expertise. This shift not only increases productivity but also contributes to a more fulfilling and enjoyable work environment, potentially leading to higher employee retention rates.
Automating Key Supply Chain Processes with Zoho
Zoho's suite of integrated applications provides a comprehensive toolkit for automating a wide range of manual processes that commonly hinder the efficiency of supply chain-dependent businesses. By strategically implementing and connecting various Zoho apps, companies can streamline their operations and achieve significant acceleration in their industry performance.
Automating Procurement: Zoho offers several tools to automate the often cumbersome procurement process. Using Zoho Creator, businesses can design custom purchase requisition forms and implement automated approval workflows, ensuring that all purchases adhere to company policies. Once approved, Zoho Flow can be configured to automatically generate purchase orders in Zoho Inventory or Zoho Books, populating the necessary details from the requisition form and sending them directly to the designated suppliers. Furthermore, Zoho Flow can automate the process of matching received invoices with the corresponding purchase orders and goods receipts in Zoho Books, streamlining the payment process and reducing the risk of discrepancies. Automated supplier communications, such as sending out requests for quotes or tracking order statuses, can also be established using Zoho Creator and Zoho Flow.
Automating Inventory Management: Maintaining optimal inventory levels and minimizing stockouts or overstocking situations can be effectively automated using Zoho Inventory in conjunction with Zoho RPA and workflow rules. Zoho Inventory allows businesses to set up automated alerts that trigger when the stock level of a particular item falls below a predefined threshold, prompting timely replenishment. Zoho RPA can be employed for continuous monitoring of inventory levels across multiple systems, providing real-time updates and flagging potential shortages or excess stock for immediate attention. Within Zoho Inventory, businesses can create workflow rules to automate tasks such as updating inventory levels automatically upon the creation of a sales order or the receipt of new stock. Zoho Inventory also supports barcode scanning and RFID labeling, which can be integrated with Zoho Flow to automate the data entry process during stocktaking and inventory movements.
Automating Order Processing and Fulfillment: The entire order processing and fulfillment cycle can be significantly accelerated through the automation capabilities of Zoho Creator and Zoho Flow. Businesses can utilize Zoho Creator to develop custom order management systems that seamlessly integrate with their e-commerce platforms or other sales channels. When a new order is placed, Zoho Flow can automate the process of retrieving the order details, updating the inventory levels in Zoho Inventory to reflect the sale, and triggering the creation of a corresponding invoice in Zoho Books. Additionally, Zoho Flow can automate the sending of order confirmations and shipping notifications to customers via Zoho CRM or other communication channels. For warehouse operations, Zoho Inventory facilitates the generation of picklists, and its integration with shipping carriers allows for automated label printing and shipment tracking.
Automating Logistics and Transportation: Managing the complexities of logistics and transportation can be streamlined using Zoho Projects and custom applications built with Zoho Creator. Businesses can leverage Zoho Creator to develop tailored logistics management applications for planning and optimizing delivery routes, taking into account factors such as distance, traffic conditions, and delivery schedules. These applications can also be used to manage driver assignments and track the real-time location of shipments. Integration with Zoho Projects allows for the monitoring of delivery progress, and automated notifications can be set up using Zoho Flow to alert relevant stakeholders about potential delays or changes in the delivery schedule. Data from transportation management systems can be integrated with Zoho Analytics to gain insights into logistics performance, identify areas for improvement, and optimize transportation costs.
Automating Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration across the supply chain can be enhanced through the use of Zoho's integrated communication tools, such as Zoho Mail, Zoho Cliq, and Zoho Connect, in conjunction with the automation capabilities of Zoho Flow. Zoho Flow can be configured to automate the sending of email notifications for various supply chain events, including order confirmations, shipment updates, low stock alerts, and delivery confirmations. Integration with Zoho Projects enables the automated assignment of tasks to team members based on specific triggers within the supply chain process, ensuring timely follow-up and accountability. Zoho Cliq and Zoho Connect facilitate real-time communication and collaboration among internal teams, suppliers, and customers, providing a centralized platform for information sharing and issue resolution.
Automating Returns Management: While Zoho does not offer a dedicated returns management application, businesses can leverage the flexibility of Zoho Creator and Zoho Flow to build custom workflows for managing the reverse logistics process. Using Zoho Creator, businesses can design custom return request forms for customers and automate the approval process based on predefined criteria. Integration with Zoho Inventory ensures that returned items are accurately added back into stock, and Zoho Books can manage the financial aspects of returns, such as processing refunds and issuing credit notes. Zoho Flow can automate communication with customers throughout the return process, providing updates on the status of their returns and any associated refunds.
Implementing Zoho for Supply Chain Automation: Key Considerations and Best Practices
Successfully implementing Zoho for supply chain automation requires careful planning, a clear understanding of existing processes, and a strategic approach to deployment.
Assess Current Supply Chain Processes: Before embarking on any automation initiative, businesses must thoroughly analyze their existing supply chain processes. This involves mapping out the flow of materials, information, and products across all stages of the supply chain. Engaging with employees from different departments to understand their pain points and identify existing bottlenecks is crucial. Businesses should also leverage data to measure key metrics such as order fulfillment times, inventory turnover rates, and shipping costs to establish a baseline for improvement.
Define Clear Automation Objectives: Establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for the automation project is essential for success. These objectives might include reducing operational costs by a certain percentage, improving order accuracy, accelerating task completion times, or enhancing overall customer experience. Clearly defined objectives provide focus and allow for the measurement of progress and the eventual return on investment.
Prioritize Automation Initiatives: Given the complexity of many supply chains, it is often advisable to adopt a phased approach to automation. Businesses should prioritize the automation of processes that are likely to yield the highest return on investment and address the most critical pain points first. This might involve starting with automating a single process, such as purchase order generation, and then gradually expanding to other areas based on the initial success and lessons learned.
Select Appropriate Zoho Applications and Integrations: Choosing the right combination of Zoho applications and ensuring seamless integration between them and with any existing third-party systems is crucial. Businesses should carefully evaluate their specific automation needs and select the Zoho applications that best fit those requirements. This might involve leveraging Zoho Inventory for inventory management, Zoho CRM for supplier relationship management, Zoho Creator for building custom applications, Zoho Flow for workflow automation and integrations, Zoho Analytics for data analysis, and Zoho Books for financial management.
Develop a Phased Implementation Plan: A gradual and iterative approach to implementing Zoho for supply chain automation minimizes risk and allows for adjustments based on feedback and results. Starting with pilot projects in selected areas of the supply chain can help to test the effectiveness of the automation solutions before a full-scale rollout. Gathering feedback from users during these initial phases is essential for refining processes and addressing any issues before expanding the automation to other areas.
Train Staff Effectively: The successful adoption of any new technology relies heavily on the ability of employees to use it effectively. Providing comprehensive training to all relevant staff members on the new Zoho systems and processes is therefore crucial. Training should cover not only the basic functionalities of the software but also how the automated processes integrate with their daily tasks and overall workflows. Ongoing support and resources should also be provided to ensure that employees feel comfortable and confident using the new systems.
Monitor Performance and Adjust: After the implementation of Zoho automation solutions, it is essential to continuously monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the effectiveness of the initiatives. Tracking metrics such as order processing time, error rates, cycle times, and customer satisfaction levels will provide valuable insights into the impact of the automation. Based on this data, businesses can identify areas for further optimization and make necessary adjustments to their Zoho configurations and workflows to maximize efficiency and profitability.
Automation of manual processes is no longer a luxury but a necessity for supply chain-dependent businesses seeking to accelerate their performance and maintain a competitive edge. The inefficiencies, errors, and limitations inherent in manual operations can significantly hinder a company's ability to respond effectively to market changes, meet customer expectations, and achieve sustainable growth.
With Zoho's comprehensive and integrated ecosystem of business applications, businesses avail a powerful solution suite for automating a wide range of critical supply chain processes. From streamlining procurement and optimizing inventory management to accelerating order processing and enhancing logistics, Zoho's suite, including Zoho Inventory, Zoho CRM, Zoho Creator, Zoho Flow, Zoho Analytics, and Zoho Books, empowers businesses to eliminate manual bottlenecks, reduce errors, lower costs, and gain unprecedented visibility across their entire supply chain.
For businesses seeking to be ahead on all of their supply chain operations and achieve accelerated growth within their industry, exploring the implementation of Zoho's comprehensive suite of applications is a strategic imperative. Erphub has helped a vast array of businesses from across industries with supply chain specific tailored solutions. Schedule a free consultation session to explore how your business can accelerate with tailored supply chain solutions.


