
The Integration Imperative - Bridging Sales, Operations, and Finance
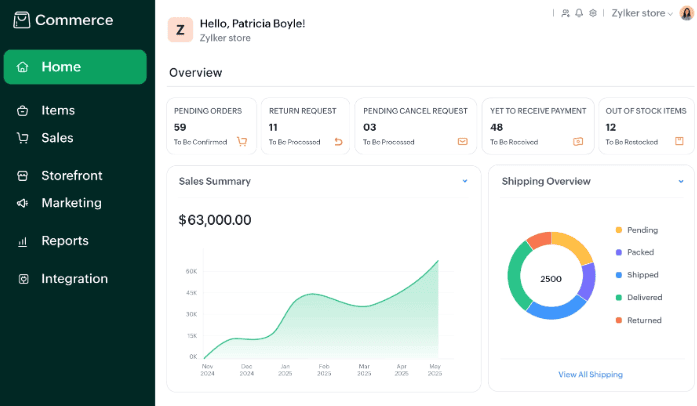
For both B2C and B2B models, the long-term success of digital commerce hinges not on the visual appeal of the website, but on the robustness of the backend processes that manage inventory, process payment, track fulfillment, and reconcile revenue. When these mission-critical functions are siloed, human intervention becomes mandatory for data transfer and reconciliation, leading to costly data errors, pervasive operational delays, and high vulnerability to stock discrepancies. An integrated ecosystem eliminates this vulnerability by automating the data exchange, ensuring that transactional data initiates immediate, corresponding updates across all organizational functions. For instance, in a B2C scenario, a single product purchase must instantly trigger a real-time inventory count update, generate an accurate sales order, and post the revenue and tax liability directly to the general ledger. Similarly, in a B2B context, the digital acceptance of a complex quote must automatically allocate stock, check the customer's credit limit, and raise a corresponding invoice, all without manual keying or departmental email exchanges. The Zoho ecosystem achieves this through native synchronization, which requires virtually no coding knowledge for setup and guarantees the automated, instant syncing of core modules. Items and Item Groups are listed seamlessly under Products, Sales Orders and Reports are synchronized into the central Orders and Reports view, and Categories and Sub-categories are linked to their respective counterparts. Crucially, all customers—both B2C retail patrons and B2B wholesale buyers—who place an order are automatically recorded as Customers in the inventory management system.
This immediate, native data flow serves as a powerful risk mitigation tool. When a sale is placed on the commerce storefront (whether B2C or B2B), the inventory core is instantaneously updated. This guarantees that stock levels reflected on the digital storefront are always accurate, proactively preventing critical issues such as overselling or fulfilling orders based on outdated data, which is especially vital in complex omnichannel environments. Overselling or stock discrepancies, common flaws in systems relying on batch updates or manual reconciliation, lead directly to order cancellations, negative customer reviews (critical in B2C reputation management), and damage to contractual B2B relationships.
The systemic value of deep integration is validated by extensive industry research. Businesses prioritizing robust automation strategies across their commerce channels report substantial, measurable uplifts in key financial indicators. Analysis of e-commerce enterprises confirms that those adopting sophisticated automation experience a significant 45% improvement in overall ROI and an 80% increase in lead generation. This translates directly into strategic capital conversion. The integrated platform drastically reduces the high OpEx (Operational Expenditure) previously dedicated to manual data reconciliation—tasks such as exporting order details from the storefront and manually importing them into the accounting system. This freed-up OpEx can be strategically reinvested into market expansion, advanced B2C personalization efforts, or enhanced B2B client service initiatives. By lowering the cost-to-serve ratio across both B2C and B2B operations, the unified platform provides exponentially greater long-term value than seemingly cheaper, non-integrated alternatives. Moreover, the accuracy derived from a single data source is essential for regulatory compliance and audit readiness in all sectors.
The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Conundrum: Fragmented vs. Integrated Architectures
Executive decisions regarding digital commerce platforms must look fundamentally beyond the initial cost of deployment. Focusing solely on upfront platform fees is a pervasive error that frequently leads to a significant and unpredictable escalation of the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over the system’s lifecycle. Fragmented technology stacks, while often presented as affordable initial investments, conceal substantial, recurring, and often crippling long-term expenses related to:
Perpetual Integration Maintenance: The continuous effort and cost required to ensure that separate applications communicate effectively as their underlying APIs evolve.
Escalating Third-Party Licensing: The necessity of acquiring and renewing separate subscriptions for every essential piece of functionality (e.g., specialized shipping calculators, CRM sync tools, tax compliance extensions).
Security Patching Burdens: The increased administrative overhead and security risk associated with managing updates and compliance across multiple disparate vendors.
Scaling Limitations: The inherent technical friction that prevents rapid, cost-effective market expansion in either the B2C or B2B domain due to fragile legacy architecture.
Understanding the true TCO requires a holistic accounting of all recurring and hidden costs — an analysis that invariably demonstrates the inherent financial efficiency and cost predictability of a natively integrated ERP-commerce architecture.
Industry analysis confirms that the failure to accurately forecast TCO is a leading cause of project distress and budget overruns in e-commerce replatforming. Enterprise commerce projects frequently report a TCO that is significantly higher than predicted, often resulting in complex and awkward budget negotiations. This reality underscores the danger of relying on the "sticker price" platform evaluation model. Fragmented systems rely heavily on external marketplaces for essential functionality—such as advanced shipping calculation, specialized accounting features, or comprehensive CRM integration. Each necessary component results in a separate recurring subscription cost, increasing vendor dependencies and creating multiple points of failure.
The complexity of inter-system dependencies introduces the single largest hidden cost. When one system in a fragmented stack (e.g., the commerce platform) updates its core API or releases a major version upgrade, all connected third-party applications and custom connectors must be simultaneously updated. In this scenario, the merchant or a hired developer team bears the entire responsibility for troubleshooting, updating, and maintaining these custom connectors, often necessitating expensive external development retainers.
The integrated ecosystem fundamentally mitigates this high-risk TCO driver by consolidating maintenance responsibility with a single vendor. The Zoho model, where Commerce, Inventory, and Books update simultaneously and are architecturally linked , internalizes this dependency risk. This drastically reduces long-term, unpredictable "break/fix" development costs, which are substantial TCO components. By converting multi-vendor dependencies into a single, managed service, the platform avoids the need for multiple third-party subscriptions for core functions like CRM and abandoned cart recovery.
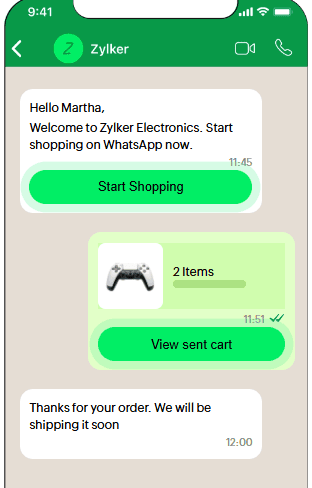
Zoho Commerce functions as the intelligent, customer-facing portal, deliberately engineered not just for high-conversion transactions but specifically to feed high-quality, structured data instantly into the core ERP backbone: Zoho Books for financial governance and Zoho Inventory for operational management. This foundational integration ensures that every sales event, whether a B2C order or a B2B invoice, is immediately registered as both an operational change (inventory depletion/allocation) and a complete financial event (revenue accrual, tax liability, and expense recording). This seamless, real-time data flow eliminates data latency and negates the necessity for manual reconciliation between departmental silos, guaranteeing a single, accurate version of the truth across the enterprise.
Commerce as the Nexus of Real-Time Financial Accuracy
The immediate synchronization between the storefront’s transactional data and the core accounting modules transforms the typically reactive accounting function into a proactive, real-time reporting mechanism essential for modern financial governance. When a sales transaction for items is posted in the Inventory management system, the corresponding changes—such as cash receipt, accounts receivable, and cost of goods sold—are automatically reflected in the Books accounting ledger. This native link ensures the organization avoids duplicate data entries and achieves seamless automation of accounting processes.
This capability is critically vital for both high-volume B2C retail and complex B2B compliance. In environments relying on manual data entry or fragile API bridges, the transfer of thousands of sales data points into an external accounting system is a major source of costly human errors, often requiring significant auditor time to resolve. The native connection between Inventory and Books ensures the financial ledger is always balanced and consistent with the operational reality of stock movement and sales. The efficiency gain from eliminating manual entry is a direct improvement in efficiency and risk management. This real-time data flow allows management to generate an extensive suite of reports, often numbering over 70 types, on demand. Instead of waiting weeks for the month-end reconciliation process to assess profitability or audit inventory write-offs, leadership teams can track real-time margin shifts, current tax liabilities, and sales velocity instantly, enabling the deployment of rapid, tactical adjustments to pricing or marketing spend based on current performance data.
Global Reach - Multi-Currency and Tax Compliance for B2B and B2C
For businesses focused on global B2C market penetration or managing complex international B2B supplier and customer relationships, the ability to seamlessly handle transactions in multiple foreign currencies from the storefront through to the general ledger is an absolute requirement. Manually managing international sales introduces significant complexity regarding exchange rate calculations and foreign tax reporting, exponentially increasing administrative overhead.
The Premium edition of the Commerce platform provides robust support for global sales, supporting multi-currency checkout options for several key foreign currencies. This functionality is powerfully complemented by the Books accounting module's capability to handle multiple currencies for the same customer. The accounting system allows the creation of sales and purchase transactions in multiple currencies and automatically manages the currency exchange rates, which can be adjusted by the finance team if needed.
The integrated currency management across both the commerce and financial platforms means that a B2C customer can execute a transaction in their local currency on the digital storefront, and the accounting system correctly records, invoices, and manages the transaction in that currency, dynamically handling exchange rate fluctuations against the organization's chosen base currency. This automation is crucial for streamlining international tax and audit trails. Cross-border commerce introduces complex challenges related to VAT, GST, and accurate exchange rate calculations. By automating currency conversion and transaction recording via native integration, the platform minimizes the risk of audit failures and significantly reduces the labor hours required for international financial compliance, a process often cited as a major roadblock for rapidly expanding small and mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) operating in both B2C and B2B global markets.
Integrated Inventory, Logistics, and Automated Fulfillment Pipelines
Operational excellence in both B2C and B2B digital commerce hinges on the ability to manage the entire logistics chain with high precision, particularly concerning real-time stock allocation and automated fulfillment routing. The Inventory management solution, tightly integrated with Commerce, transcends basic stock tracking; it transforms into a sophisticated command center for omnichannel sales, multi-location management, and automated dropshipping workflows. This unified operational core ensures that customer expectations regarding shipping times and product availability are consistently met, directly protecting brand reputation and mitigating financial losses associated with fulfillment errors.
Real-Time Stock Synchronization and Omnichannel Management
The capability to synchronize stock on hand automatically across all selling channels—including the core Commerce site (B2C/B2B), popular third-party marketplaces (B2C focus), and even physical retail/distribution locations (omnichannel focus)—is fundamental for scaling operations and maintaining data integrity. When a business leverages multiple online sales channels (e.g., their own storefront plus a major e-commerce retail platform), the integrated system guarantees that the stock on hand will be automatically updated across all integrated channels whenever there is a change in its stock level. This process is instantaneous, ensuring a sales order is automatically generated for an unfulfilled sale made in any of the channels.
This synchronization functionality directly addresses the core dilemma of modern omnichannel retail: avoiding the costly and reputation-damaging stockout or overselling scenarios. When a B2C sale is placed on the core commerce site, that action instantly depletes the stock count visible simultaneously on a separate marketplace, all managed centrally within the Inventory application. Similarly, when a B2B partner places a large order through the Customer Portal, that stock is instantly reserved and removed from the available count for all other channels, preventing double allocation. Executives often hesitate to expand sales to multiple marketplaces due to the complexity and cost of manually or externally managing this synchronization. Because the Inventory solution provides native, real-time synchronization, businesses can confidently leverage multiple popular sales channels without fearing stock errors, thereby directly fueling sales velocity and accelerating market penetration with high reliability.
Automated Fulfillment, Drop Shipping, and Carrier Integration
The integrated Inventory solution facilitates advanced logistics scenarios essential for managing the high variability of modern commerce, including seamless integration with major shipping carriers and the ability to automate dropshipment workflows, which can significantly optimize capital efficiency by reducing the necessity to hold physical stock. Efficient B2C and B2B supply chains require flexibility in how orders are fulfilled. The platform supports a wide range of global shipping carriers , including direct integration with major entities like UPS for domestic shipping across various regions.
By integrating directly with these carriers, the system can automate the entire post-purchase process: generating shipping labels, calculating live rates , tracking shipments, and communicating status updates back to the customer via linked CRM and marketing automation workflows. This high level of automation reduces reliance on manual fulfillment coordination, which is notoriously prone to error. Furthermore, drop shipping—a supply chain management technique in which the retailer transfers customer orders and shipment details to a third party —is natively managed within the Inventory platform.
The utility of the Inventory solution is further enhanced by its dynamic workflow automation capabilities. Workflow rules allow for sophisticated automation based on predefined conditions, such as triggering emails, field updates, or custom functions. A powerful application of this technology is the configuration of automated shipment routing rules: if the stock for a product runs out in Warehouse A (relevant to both B2C and B2B orders), the workflow can be designed to automatically check stock levels in Warehouse B, or even trigger a drop-shipment purchase order to a pre-approved vendor. This dynamic, logic-driven response maximizes fulfillment speed and minimizes the human intervention required, ensuring consistent delivery standards even under high-demand B2C spikes or complex B2B fulfillment deadlines.

