
As departments and teams autonomously adopt their own cloud applications and services, user identities and access rights become fragmented across disparate systems. This decentralization creates significant security blind spots and leads to operational inefficiencies. The manual processes often required to manage these scattered identities are time-consuming and prone to human error, which can result in security risks and compliance failures. Without a single source of truth for identity data, organizations struggle to maintain granular control over access rights and ensure consistency. This complex, fragmented landscape increases the risk of unauthorized access, complicates compliance with evolving data privacy regulations, and raises the total cost of IT management.
Legacy security architectures, built to defend a fixed network boundary, are proving inadequate for an environment where users, applications, and data are dispersed across a multitude of platforms and locations. In this new paradigm, identity has emerged as the new security perimeter, a fundamental aspect of cybersecurity and a mission-critical component of operational efficiency. The strategic management of digital identities and access rights is now considered a cornerstone of business resilience, with a significant majority of security leaders recognizing its extreme importance to their overall security strategies. This report provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and implementing a cloud-native identity platform to secure the contemporary workforce.

Cloud-native Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a strategic evolution of traditional on-premise systems. It is not merely a hosted version of legacy software but a complete framework designed from the ground up for the dynamic, decentralized nature of the cloud. Its architecture leverages the inherent scalability and flexibility of cloud computing to manage digital identities and enforce access rights across multi-cloud and hybrid environments. This approach is built to secure a fluid landscape where the traditional security perimeter has dissolved, and access is needed from any device, anywhere.
At its core, cloud-native IAM is founded on three primary concepts that form the basis of a secure access framework :
Identity: This pertains to the unique digital representation of a user or entity within a system. This identity is the central point from which all access decisions are made.
Authentication: This is the process of verifying an identity's claim through robust mechanisms. It confirms that the right person or entity is attempting to access a resource. This is often enhanced with technologies like multi-factor authentication (MFA) to provide a higher level of assurance beyond a simple password.
Authorization: Following successful authentication, authorization determines the specific levels of permission and access rights granted to the verified identity. It ensures that a user can only access the applications, data, and resources that are essential for their role and responsibilities.
Modern cloud-native IAM systems are also adaptive and context-aware, making real-time access decisions based on multiple factors such as user behavior, device, and location. This sophisticated approach provides a solid defense against evolving cyber threats.
The transition from conventional, on-premise IAM to a cloud-native platform is no longer a luxury but a necessity for business continuity and growth. This shift offers significant advantages over legacy systems by enabling organizations to secure their operations more effectively and efficiently. A key benefit is the enhanced security posture. Cloud IAM strengthens protection by continuously monitoring access across platforms and implementing robust, identity-based controls. In a world where Zero Trust architectures are becoming the standard, this constant verification is crucial.
Furthermore, cloud IAM provides unparalleled scalability and flexibility. Organizations can expand their IAM capabilities to accommodate a growing workforce or an increasing number of applications without the need for additional hardware or complex infrastructure upgrades. This is particularly critical for supporting remote and hybrid work models, as it enables secure, location- and device-agnostic access for all employees. Beyond security and agility, the business case is also driven by cost efficiency. Cloud-based IAM reduces on-premises maintenance expenses and often operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can lead to significant cost savings compared to the high upfront capital expenditure of traditional systems. The market for IAM is expected to grow at about 13%, reaching an estimated value of over $24 billion by the end of 2025, underscoring the urgency for businesses to invest in these cutting-edge technologies to secure their digital assets and ensure compliance with evolving regulatory requirements.
The migration to cloud-native IAM is more than a simple technological upgrade; it represents a fundamental paradigm shift in cybersecurity philosophy. Legacy IAM systems were designed to protect a fixed network perimeter, with the assumption that everything and everyone inside the network could be trusted. This model is fundamentally flawed in today's environment, where the workforce is distributed and the most critical data and applications reside in the cloud. A traditional perimeter-based defense system leaves organizations vulnerable to insider threats, compromised credentials, or lateral movement from a breached device that has already gained a foothold inside the network.
A cloud-native IAM solution addresses this core weakness by operating on an identity-centric security model. By managing identities centrally, irrespective of where the users or applications are located, it enforces a uniform and consistent security posture across all environments, whether on-premises, hybrid, or multi-cloud. This capability is not merely an efficiency tool; it is a strategic enabler of business continuity and a prerequisite for modern security that a traditional system cannot achieve. An organization that adopts this model is not just securing its systems; it is enabling its workforce to be productive and agile in a new, borderless digital landscape, all while significantly reducing its risk profile.
The Zero Trust framework is a revolutionary cybersecurity philosophy built on the foundational principle of "never trust, always verify". It fundamentally shifts the security mindset away from traditional, perimeter-based models that automatically trust anyone or anything inside the network. This legacy approach is considered flawed because it leaves open the possibility for unchecked bad actors to roam freely within a corporate network once they have breached the initial perimeter.
In contrast, Zero Trust assumes a network has already been compromised. Every access request, regardless of whether it originates from inside or outside the network, must be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated before access is granted. This strict approach is essential for mitigating the risks posed by sophisticated attacks, insider threats, and the complexities of modern multi-cloud environments. The Zero Trust model advocates for several key strategies to minimize risk, including the principle of least privilege, micro-segmentation of the IT environment into secure zones, and just-in-time access, which limits privileged access to specific timeframes. For an organization to truly secure itself in the digital era, adopting Zero Trust is not just a best practice; it is a strategic imperative.
IAM as the Cornerstone of Zero Trust
Identity and Access Management is not merely a supporting technology for Zero Trust; it is its foundational pillar and primary enforcement mechanism. The core principles of Zero Trust, such as explicit verification, least privilege access, and continuous monitoring, are implemented and enforced directly through a robust IAM platform. Without a comprehensive IAM solution, an organization cannot effectively implement Zero Trust.
A centralized IAM solution provides the necessary framework for controlling user access to network resources. It enables organizations to verify user identities, assign appropriate access privileges based on their role, and enforce granular policies that govern access to sensitive data and applications. By centralizing these controls, the IAM platform helps to enforce the "principle of least privilege," which dictates that users are only granted the minimum access privileges required to perform their job functions. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data, even in the event of a user's account being compromised. An effective IAM platform provides the foundation for continuous authentication, access control, and policy enforcement across all network resources, making it an indispensable part of a Zero Trust architecture.

While a comprehensive IAM solution manages standard workforce identities and access, a truly robust Zero Trust architecture requires a complementary focus on privileged access. This is where Privileged Access Management (PAM) comes into play. PAM is a specialized subset of IAM designed to secure high-risk accounts—such as those used by IT administrators, developers, or third-party vendors—that have elevated privileges and access to an organization's most critical assets. A compromised privileged account can have devastating consequences, as it can be used to move laterally within the network and access sensitive data, a threat far more severe than a standard account breach.
By integrating the concepts of least privilege and just-in-time (JIT) access, a PAM solution ensures that even privileged users are not implicitly trusted. It provides a heightened layer of security by enforcing a request-approve workflow for credential release and limiting privileged access to the specific duration required for a task. This approach aligns perfectly with the Zero Trust philosophy. The distinction between IAM and PAM is therefore one of scope and specialization: IAM provides the broad, foundational security for the entire workforce, while PAM provides a specialized, hardened layer of security for the most critical identities and systems. A unified security posture is achieved when both are implemented in concert. Notably, Zoho's parent company, ManageEngine, offers a dedicated PAM solution called PAM360, which provides a cohesive vision for a complete security strategy. This allows an organization to start with a robust IAM platform like Zoho Identity360 and then layer on a specialized PAM solution for a more mature security posture, all from a single vendor ecosystem. This demonstrates a deep, multi-layered approach to modern cybersecurity.
Securing the Continuous Journey to Zero Trust
The implementation of a Zero Trust framework is not a one-time deployment but a continuous process of verification and adaptation. The cornerstone of this journey is a cloud-native IAM solution with a unified approach to identity management. This is because traditional, on-premise systems are often too rigid and fragmented to support the dynamic nature of Zero Trust. The need for constant authentication, granular policy enforcement, and real-time monitoring across a dispersed workforce necessitates a platform that is inherently scalable, flexible, and centralized.
The relationship between IAM and PAM is a critical component of this continuous security journey. Where IAM establishes the base security for every identity and access point, PAM adds a vital, specialized layer of defense for the highest-risk accounts. A vendor that provides both solutions, as is the case within the Zoho/ManageEngine ecosystem, allows an organization to build its Zero Trust architecture seamlessly. This approach eliminates the complexities and security gaps that can arise from integrating disparate vendor solutions. It allows for a single, centralized management console, consistent policy enforcement across all users, and a unified audit trail for compliance and forensic analysis. By starting with a comprehensive, cloud-native IAM solution and understanding its strategic relationship with privileged access management, a business can build a robust, scalable, and resilient security posture that is fully prepared for the challenges of the modern digital landscape.
Zoho Identity 360
Zoho Identity360 is a comprehensive, fully cloud-native IAM solution designed to safeguard an organization's digital landscape while simplifying user identity management. Its architecture is purpose-built for the modern enterprise, eliminating the need to worry about infrastructure costs or ongoing maintenance. This cloud-powered approach provides businesses with a flexible and scalable platform that can grow alongside their needs, effortlessly managing identities and access across hybrid environments.
A key strength of Identity360 is its modular design. The platform offers a range of components that can be tailored to address diverse organizational challenges, allowing businesses to pay only for what they need. This "IAM on your terms" philosophy makes it a highly adaptable solution for companies of all sizes and industries. The platform's seamless integration with a wide range of third-party applications and directories ensures smooth interoperability across an organization's existing technology stack, creating a unified and cohesive identity management experience.
Centralized Identity and Lifecycle Management
The foundation of Zoho Identity360 is its Universal Directory, a built-in feature that acts as a single source of truth for all identity data across integrated applications and services. This capability directly addresses the problem of fragmented identities and a lack of centralized visibility, which is a major challenge for organizations today. By centralizing user information, the Universal Directory enables administrators to manage user identities and permissions from a single, secure console, regardless of the user's location or the applications they need to access.
Building on this centralized foundation, the platform's Lifecycle Management features, enabled by identity orchestration and smart templates, automate the entire user journey from onboarding to offboarding. This automation is critical for minimizing the security risks and manual effort associated with manual provisioning and de-provisioning. It ensures that new employees are granted the correct access on their first day and that access is promptly revoked when an employee leaves or changes roles. This streamlined approach enhances both security and operational efficiency by reducing the risk of orphaned accounts and unauthorized access. Admins can use predefined templates with role-specific rules to enable one-click user setup and automatically modify access permissions and assign licenses across various applications.
Unifying Access with Seamless Single Sign-On (SSO)
Zoho Identity360's Single Sign-On (SSO) capability is a cornerstone of its value proposition for workforce productivity and security. This feature boosts efficiency by providing secure, one-click access to all necessary applications with a single set of credentials. For end-users, this eliminates the frustration of password fatigue and the time-consuming process of managing multiple login credentials. For administrators, it reduces the number of password-related helpdesk calls and simplifies user management.
The solution supports a broad spectrum of industry-standard protocols, including SAML 2.0, OAuth, and OpenID Connect, which allows for seamless integration with a wide range of pre-integrated and custom cloud applications. The SSO process within Identity360 is fortified by a mandatory two-step verification, ensuring an enhanced security posture. This process involves a primary authentication step where a user's credentials are verified, followed by a secondary authentication step that requires verification with an admin-configured multi-factor authentication method. This dual-layer approach ensures that security is not compromised for the sake of a simplified user experience.
Fortifying Security with Modern Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
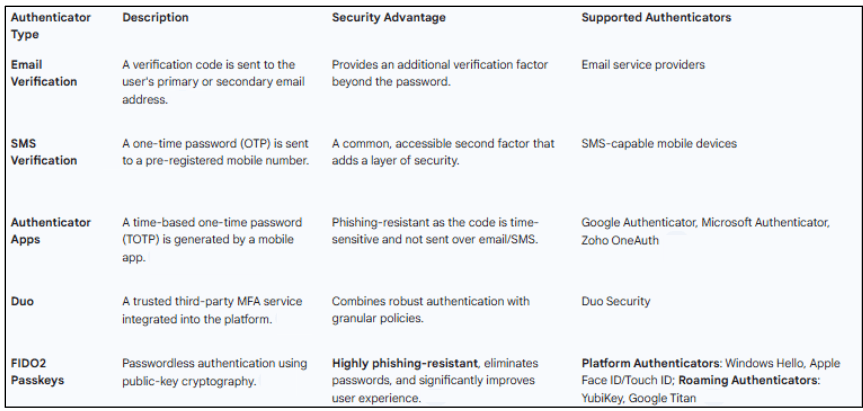
Zoho Identity360 fortifies an organization's security with a comprehensive, phishing-resistant MFA framework. This additional layer of security is designed to ensure that only authorized users gain access, shielding valuable data from potential cyber threats. The platform supports a wide array of authentication methods, catering to both traditional and modern security requirements.
Users can choose from a robust selection of authenticators, including time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) from apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, and Zoho OneAuth, as well as SMS and email-based verification. A particular focus is placed on the adoption of high-assurance, phishing-resistant methods like FIDO2 passkeys, which aligns with the industry trend towards eliminating traditional passwords. These passkeys utilize public-key cryptography and are compatible with both platform authenticators (such as Windows Hello and Apple Face ID) and roaming authenticators (like YubiKeys). The inclusion of Duo as an MFA option further extends the platform's flexibility and integration capabilities. This comprehensive approach to MFA ensures that organizations can implement a strong authentication strategy that is both secure and user-friendly, reducing the risk of credential theft and account takeovers.

